Medication & Research
Acute chest crisis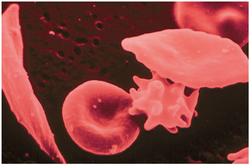
Management is similar to vaso-occlusive crisis, with the addition of antibiotics (usually a quinolone or macrolide, since cell wall-deficient ["atypical"] bacteria are thought to contribute to the syndrome),[46] oxygen supplementation for hypoxia, and close observation. Should the pulmonary infiltrate worsen or the oxygen requirements increase, simple blood transfusion or exchange transfusion is indicated. The latter involves the exchange of a significant portion of the patients red cell mass for normal red cells, which decreases the percent of haemoglobin S in the patient's blood
|
ESA Drugs Treat Anemia By Stimulating Red Blood Cell Production
If you have anemia your blood isn’t able to carry and distribute enough oxygen to different tissues and organs. As a result, you may feel tired or have other symptoms depending on the severity of anemia. People with severe anemia may feel tired, fatigued or experience shortness of breath, which can cause problems carrying out routine activities. Erythropoietin is a natural substance made by certain kidney cells. These kidney cells are very sensitive to the amount of oxygen in your blood. When these cells determine that your oxygen level is low, they release more erythropoietin. The erythropoietin then signals your bone marrow to make more red blood cells in order to carry more oxygen throughout the body.
Erythropoiesis-stimulating Agents Available in the United StatesTrade NameGeneric Name (Brand)ProcritErythropoietin alfaEpogenErythropoietin alfaAranespDarbepoetin alfaProduct Package Inserts. August 2008.3-5 Sometimes the kidneys cannot make enough erythropoietin. If this is the case, your doctor may prescribe an ESA. Synthetic ESA drugs act like the natural erythropoietin, and are given to help the body produce more red blood cells and raise hemoglobin levels. Currently there are two ESA drugs available in the United States to treat anemia: erythropoietin alfa, which is also referred to by the brand names Epogen and Procrit, and darbepoetin alfa, which is also referred to by the brand name Aranesp. What Types of Patients Receive ESAs? ESAs are approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat anemia which has been caused by cancer chemotherapy treatment, kidney failure, or a drug used to treat AIDS. Erythropoietin has also been approved for use to increase the red blood cell count in anemic patients who are scheduled to have surgery. This can decrease the need for blood transfusions following surgery. Though not yet approved by the FDA, ESAs have also been shown to be of benefit in managing anemia in elderly people, in people with inflammatory bowel disease, and in people with rheumatoid arthritis. |
Epoetin alfa
Epoetin alfa is a synthetic form of a protein produced by the kidneys that stimulates the production and release of red blood cells. A similar drug, darepoetin alpha, is available with the same properties, but it remains active longer and so requires fewer injections each week. Because epoetin alfa is approved for more types of anemia than darepoetin, this discussion deals only with the older drug. Epoetin alpha is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the following uses:
In addition, epoetin alpha may be useful in anemia from many other causes. These include but are not limited to anemia of prematurity, sickle cell anemia, and the anemia associated withrheumatoid arthritis. The drug has been abused by athletes due to the theory that increasing the red blood cell count improves athletic performance. The potential benefits of misuse of the drug are limited, and the risks are significant. The United States and International Olympic Committees and the National Collegiate Athletic Association consider the use of epoetin alfa to enhance athletic ergogenic potential inappropriate and unacceptable because its use by athletes is contrary to the rules and ethical principles of athletic competition. As of the early 200s, tests to detect the misuse of epoetin alfa by athletes are increasingly reliable. |
